甘肃洛坝铅锌矿选矿流程考察与优化
周贺鹏 , 1 , 2 , 胡洁 1 , 段朝阳 3 , 邓攀 3 , 钟志刚 1 , 张永兵 1
1. 江西理工大学资源与环境工程学院,江西 赣州 341000
2. 江西省矿业工程重点实验室,江西 赣州 341000
3. 甘肃洛坝有色金属集团有限公司,甘肃 陇南 742500
Investigation and Optimization of Processing Flowsheet for a Luoba Lead-zinc Mine in Gansu Province
ZHOU Hepeng , 1 , 2 , HU Jie 1 , DUAN Chaoyang 3 , DENG Pan 3 , ZHONG Zhigang 1 , ZHANG Yongbing 1
1. Faculty of Resource and Environmental Engineering,Jiangxi University of Science and Technology,Ganzhou 341000,Jiangxi,China
2. Jiangxi Key Laboratory of Mining Engineering,Ganzhou 341000,Jiangxi,China
3. Gansu Luoba Nonferrous Metal Group Co. ,Ltd. ,Longnan 742500,Gansu,China
收稿日期: 2018-03-21
修回日期: 2019-04-25
网络出版日期: 2019-10-29
基金资助:
国家重点研发计划项目“含砷铜基多金属固废预脱杂与定向矿化技术” . 2018YFC1901602-3 应用示范” . 2018-GX-A7 青海省重点企业技术创新项目“高原高寒缺氧条件下铅锌硫化矿高浓度浮选分离技术应用” . JC-2017-37
Received: 2018-03-21
Revised: 2019-04-25
Online: 2019-10-29
作者简介 About authors
周贺鹏(1986-),男,江西吉安人,副教授,从事微细粒矿物分选理论与工艺研究工作zhp0919@163.com
, E-mail:zhp0919@163.com
摘要
我国铅锌矿产资源丰富,但其自然禀赋差且矿物组成复杂,导致其综合回收利用难度大。甘肃洛坝铅锌矿是一座含铅锌且伴生有少量银、硫的泥岩—细碎屑岩型铅锌矿床,因其矿石性质复杂,较早期形成的矿石性质发生明显变化,导致铅锌分选指标及精矿质量下降。为解决现有选矿生产过程中存在的问题,寻找适宜的改进措施和方法,以提高铅锌资源综合利用效率,在研究矿石性质的基础上开展了详细的工艺流程考察。研究结果表明:矿石中碳质、硅质等脉石矿物含量升高,碎磨过程易于泥化,且吸附性能和可浮性好,这些是影响铅锌分选指标的主要因素;通过优化碎磨工艺参数,减少了碳质、硅质等脉石矿物的泥化程度;在浮选工艺中添加适宜抑制剂,并采用高选择性的铅、锌矿物捕收剂,可显著提高铅、锌精矿品位和质量,大幅提高铅、锌回收率,从而实现该复杂含碳低品位铅锌资源的高效综合回收,并为同类矿产资源的选矿回收提供参考依据。
关键词:
铅锌硫化矿 流程考察 磨矿分级 工艺优化 细粒浮选 高效回收
Abstract
The lead and zinc mineral resources are very abundance in China,but the lead-zinc metal quantity is much short for further mining.The resources are not of natural endowment,with difficulty of utilization.Type of lead-zinc deposit is variety and associated elements are rich.Sulfide minerals have similar interface properties and are difficult to separate.Widespread as the occurrence of resource is,the ores are mostly very low-grade,complexity of multi-components and difficult of separation.All of this up make it difficult to recover such resources efficiently and comprehensively.It is necessary to carry out systematic process optimization and technical research in order to improve the comprehensive utilization.The Luoba lead-zinc deposit in Gansu Province is a mudstone-fine clastic lead-zinc deposit,associated with a small amount of silver and sulfur.With the long-term exploitation and utilization,the valuable metal content of lead and zinc in the ore decreases,while the content of carbonaceous and siliceous minerals increases,which brings great interference to the separation and recovery of lead and zinc.There are some problems in lead and zinc concentrate production,such as lead concentrate grade decrease,zinc concentrate containing excessive silicon.As a result,the present mineral processing technology and reagent system can’t adapt to the change of ore properties well.Therefore,a systematic process optimization and technical research should be carried out to find out the quality decline of concentrate and the possible problems in the process of concentration,and to explore the difficulties and physical factors in the recovery of lead and zinc flotation,so as to improve the comprehensive utilization level of resources.On the basis of detailed understanding of mineral processing technology and production status,an overall processing flowsheet investigation was conducted.It has been studied that the technical parameters and production conditions of each operation of grinding and floating process.Then the distribution of useful and harmful elements was identified.The problems existing in the production process were analyzed,the physical factors concerning the grade and quality of lead and zinc concentrate were proved.Then put forward a specific improvement program in order to optimize the existing process and technical conditions,and to provide a high efficiency foundation for carbolic lead-zinc resources recovery.The results show that the carbonaceous minerals,such as aphanitic graphite,are of high content in the ore.It is easy to be mud in the grinding process,and has good floatability and adsorption performance.Because of the interaction between the carbonaceous minerals and lead-zinc minerals,the adsorbing quantity of collectors for the lead-zinc minerals in slurry system was less than that of collectors without carbonaceous minerals.The carbonaceous minerals,such as aphanitic graphite,finally entered the concentrates,affecting the recovery and quality of lead and zinc minerals.High-alkali speed flotation technology,has solved the concentration recovery of lead and zinc mineral.But the content of silicon and carbon in lead and zinc concentrates is high. So,it needs to search some appropriate inhibitors in the separation process,to strengthening inhibition of zinc-sulfide minerals.At the same time,it is necessary to appropriately optimize the parameters of grinding process,to reduce the degree of argillation of the carbonaceous and siliceous gangue minerals.In order to improve the grade and quality of lead and zinc concentrate,it is necessary to find suitable collectors and reduce the viscosity of flotation foam.Through put forward a specific improvement program in order to optimize the existing process and technical conditions,and to provide a high efficiency foundation for carbolic lead-zinc resources recovery.
Keywords:
lead-zinc sulphide ore process flowsheet investigation grinding classification process optimization fine particles flotation high efficiency recovery
本文引用格式
周贺鹏, 胡洁, 段朝阳, 邓攀, 钟志刚, 张永兵. 甘肃洛坝铅锌矿选矿流程考察与优化 [J]. 黄金科学技术 , 2019, 27(5): 696-703 doi:10.11872/j.issn.1005-2518.2019.05.696
ZHOU Hepeng, HU Jie, DUAN Chaoyang, DENG Pan, ZHONG Zhigang, ZHANG Yongbing. Investigation and Optimization of Processing Flowsheet for a Luoba Lead-zinc Mine in Gansu Province [J]. Gold Science and Technology
铅锌是国民经济与科技发展的保障性资源,铅锌矿产资源的高效开发利用是国家重大战略需求[1 ] 。我国铅锌资源丰富,已查明的铅金属量达8 546.77×104 t,锌金属量达17 798.89×104 t[2 ] ,但目前开发的铅锌矿床中,大多矿石类型复杂,共伴生组分多[3 ,4 ,5 ] ,综合回收难度大,而铅锌硫化矿物(如方铅矿、闪锌矿和黄铁矿等)界面性质相近,浮选分离存在一定的困难[6 ] ,导致该类资源高效综合利用难度增加。随着国民经济的发展,各行业对铅锌资源的需求量也在不断增加,需进一步加强对铅锌资源合理、高效的开发利用[7 ,8 ] 。
甘肃洛坝铅锌矿是一座含铅锌且伴生有少量银、硫的泥岩—细碎屑岩型铅锌矿床[9 ,10 ] ,近年来随着铅锌资源的不断开发,铅锌矿石性质发生显著变化,铅、锌品位下降,而C、Si和Fe等杂质元素含量明显升高,使得选矿生产存在铅精矿品位下降、锌精矿含硅超标等问题。为查明精矿质量下降的原因,以及选矿流程中可能存在的问题,探索铅锌浮选回收的难点及物性因素,进行系统的选矿流程考察和矿石性质分析,以期为该铅锌资源的高效回收提供有益指导。
1 矿石性质
对洛坝铅锌矿的原矿进行了化学多元素分析和矿物组成分析,结果见表1 和表2 。
由表1 可知,Pb和Zn是洛坝矿主要的回收元素;伴生的Cu、S和Ag等元素含量低,回收价值不大;矿石中碳质含量较高,因其具较好的可浮性和吸附性能,对铅锌选别产生较大影响[11 ,12 ] ;由CaO、SiO2 、Al2 O3 和MgO等化合物组成的碳酸盐—硅酸盐类矿物属于脉石矿物,其易碎磨泥化,对铅锌精矿产生干扰[13 ] ;此外,矿石中Fe含量较高,主要以菱铁矿形式存在,难以通过选矿回收。
由表2 可知,铅锌矿物主要赋存在方铅矿和闪锌矿中,少量为车轮矿和红锌矿,同时还存在极少量的含锌菱铁矿;硫化矿物以黄铁矿为主,黄铜矿、毒砂、辉砷镍矿和银黝铜矿等矿物含量稀少;脉石矿物以石英、方解石、菱铁矿、铁白云石和白云石等碳酸盐矿物为主,其次为白云母和高岭石等硅酸盐矿物。因脉石矿物组成复杂,易碎磨泥化,对铅锌回收产生较大影响。
2 选矿工艺现状
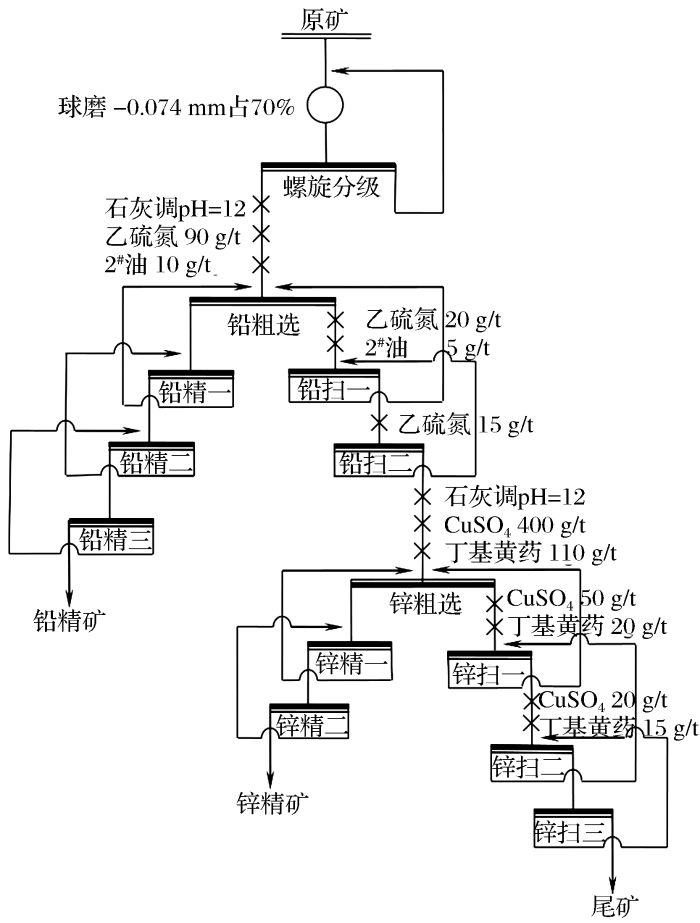
选矿厂铅锌生产工艺包括磨矿分级和浮选工艺两段流程,生产工艺流程如图1 所示,生产指标见表3 。磨矿分级系统采用φ 3 200×3 600 mm型球磨机和φ 3 000 mm单螺旋高堰式分级机组成的一段闭路磨矿流程;浮选工艺采用“高碱铅锌优先浮选”工艺流程为主体,即石灰调节矿浆pH值达12以上,以乙硫氮作铅矿物捕收剂优先选铅,铅尾采用CuSO4 作活化剂、丁基黄药作捕收剂、2# 油作起泡剂进行锌矿物浮选。浮选工艺流程为铅浮选一粗三精两扫和锌浮选一粗两精三扫。
图1
图1
选厂选矿工艺流程图
Fig.1
Flowsheet of mineral processing technology in concentrator
矿石中铅、锌得到了较好的富集回收,但与其他相似铅锌矿相比[14 ,15 ] ,铅锌精矿的品位仍有一定的提升空间,且铅锌精矿中硅含量较高,影响产品质量,因此需进行系统的选矿工艺流程考察,找出影响铅、锌选别的主要因素及其解决方案。
3 选矿工艺流程考察
3.1 磨矿分级作业考察
对磨矿分级作业产品进行了粒度组成分析,结果见表4 。
原矿经一段闭路磨矿后螺旋分级机溢流产品中-74 μm粒级占69.33%,-45 μm粒级占55.19%,远超过正常的细粒分布水平[16 ] 。+45 μm粒级铅含量较低,质量分数在0.10%~0.13%范围内,而-45 μm粒级铅质量分数高达1%,相比原矿富集了近一倍,而在此微细粒级中铅分布率高达91.03%,表明铅矿物易于碎磨和解离,这种碎磨和嵌布特性有利于铅的浮选回收。然而,由于绝大多数铅的入选粒级为-45 μm微细粒级,不利于铅与其他微细粒脉石矿物及易浮杂质矿物等之间的分离,影响了铅精矿品位的提高。锌和杂质硅矿物在各粒级中的品位分布较均匀,差异不大。
螺旋分级机的返砂比为73.39%,而一段闭路磨矿分级机的返砂比通常在150%~350%之间[17 ] ,由此可见螺旋分级机的返砂比严重偏低,循环负荷量较小,这不仅影响球磨机的磨矿效率,而且易加重细粒矿物过粉碎现象。
3.2 浮选作业考察
对选矿产品(铅精矿、选铅尾矿、锌精矿和总尾矿)进行了粒度组成分析,结果见表5 。
铅精矿中回收的主金属铅以细粒级为主,占精矿总铅的71.67%,中、粗粒级铅含量较低;而选铅尾矿中铅金属主要呈两头粗、中间细的“哑铃型”曲线分布,微细粒级与粗粒级均占30%~40%。由此可见,因碎磨过程铅矿物粒度过细,导致铅精矿浮选品位与回收率均受到一定的影响,主要表现在过细粒级并没有完全被回收在铅精矿中,限制了铅回收率的升高;过细粒级的目的矿物与细粒级脉石及杂质矿物之间较难分离,也会影响精矿品位。此外,尾矿中损失的铅金属有约30%以粗粒级存在,这与其单体未充分解离相关,进而影响铅的回收。
铅精矿中所含的锌主要为细粒级,因此要降低铅精矿中的锌含量,需从细粒级锌矿物入手,添加少量的抑制剂进行细粒锌的强化抑制[18 ,19 ] 。锌在锌精矿和总尾矿中的分布基本一致,以细粒级为主。锌精矿中回收的锌主要为细粒级,且尾矿中损失的锌矿物更细,为进一步提高锌回收率,需从细粒级入手,强化细粒锌的回收。
4 讨论与建议
通过流程考察,对生产工艺进行了系统查定,详细分析了磨浮生产现状,查明了现有生产过程中存在的问题,并归纳了原因,提出了相应的建议。
(1)原矿为含铅锌且伴生有少量银、硫的泥岩—细碎屑岩型铅锌矿,铅锌矿物主要以方铅矿和闪锌矿形式产出。脉石矿物以石英及方解石、菱铁矿、铁白云石和白云石等碳酸盐矿物为主,其次为白云母和高岭石等硅酸盐矿物。
(2)入磨矿石细粒物料偏多,筛分工艺有待优化。入磨给料皮带上粉状细粒矿石增多,其中-74 μm粒级含量达7.68%,-150 μm粒级含量更高,而现有筛分工艺未根据原矿粒度组成制定相应的筛分流程,直接将细粒物料与粗粒矿石一并入磨,加剧了细粒矿石的过磨现象[20 ] ,导致分级溢流中-38 μm微细粒级含量增多,达48.88%。建议增加一套2 mm的细筛湿筛,将筛下产品与磨矿产品合并,同时给入螺旋分级机分级,及时分离出合格粒级,减少过磨现象。
(3)磨矿工艺过粉碎严重,磨矿参数有待优化。原矿属于低铅锌含碳的碳酸盐—硅酸盐混合型铅锌矿,矿石中石英、闪石和长石等硅酸盐脉石矿物难以碎磨,而隐晶质石墨、方解石、云母和方铅矿等易于碎磨,且铅锌矿物普遍呈粒状和块状等构造沿脉石矿物裂隙充填或交代连生,易造成铅、锌及部分隐晶质石墨、方解石和云母等矿物易于过磨。而铅锌及脉石矿物的过粉碎,不仅造成浮选矿浆黏度增加,而且微细粒矿物间的分离难度增大,碳质及细粒脉石粘滞夹带或疏水上浮进入精矿,影响精矿品位和质量[21 ] 。基于此类矿石性质,考虑到磨机排矿中-74 μm含量已达43.93%,现场进一步降低磨矿浓度(由目前的75%降低至70%),显著减轻细粒矿石的过粉碎现象。
(4)返砂比与分级效率偏低,分级参数有待调整。螺旋分级机返砂比为73.39%,比正常值(150%~350%)明显偏低,这不仅影响磨机的磨矿效率,而且易加重细粒级过粉碎[22 ] ,主要原因是球磨机选型偏大和矿石易磨碎,使得矿石在球磨机一次性磨细概率增大,造成返砂量减小而微细粒级增多。计算的分级质效率为59.47%,比螺旋分级机普遍正常值(60%~65%)略低,主要原因是分级浓度偏低,如分级溢流浓度仅为36.23%,比正常值(38%~42%)偏低。因此,可适度调小磨机排矿口水量,以提高进入分级机的分级浓度[23 ] 。
(5)开发高选择性药剂,降低浮选过程的泡沫黏度,从而提高铅、锌精矿品位和质量。铅、锌精矿单体含量分别为94.4%和90.9%,铅精矿中的锌与锌精矿中的铅主要呈连生体形态,部分黄铁矿为连生体,脉石矿物普遍为隐晶质石墨、石英、方解石和云母等,但铅精矿中碳质脉石矿物含量更高,锌精矿中硅质脉石矿物含量更高;铅、锌精矿中黄铁矿与脉石矿物杂质粒度微细(0.01~0.05 mm)。据此,要实现铅、锌精矿品位的进一步提高,需强化含硅脉石矿物的抑制,而隐晶质石墨和黄铁矿通过降低矿浆与泡沫黏度的方式来解决[24 ] 。
5 结论
(1)原矿为泥岩—细碎屑岩型铅锌矿,铅锌矿物主要为方铅矿和闪锌矿,脉石矿物为碳酸盐—硅酸盐类矿物,因隐晶质石墨等碳质矿物具有较好的可浮性和吸附性能,而方解石、云母等硅质脉石矿物又易于过磨泥化,对铅、锌选别回收和精矿质量产生一定的影响。
(2)碎磨后的入选矿石微细粒级含量较高,且杂质硅在细粒级的分布率较高,不仅造成浮选矿浆黏度升高,而且微细粒矿物间的分离难度增大,碳质及细粒脉石粘滞夹带或疏水上浮进入精矿,影响精矿品位和质量。微细粒含碳、硅等杂质矿物易于粘滞夹带和疏水上浮进入精矿,影响铅、锌精矿品位和质量。
(3)铅、锌矿物回收以细粒为主,而尾矿中铅锌损失也多为细粒级,因此为提高铅锌主金属的回收率,需进一步加强细粒与微细粒主金属矿物的回收。
参考文献
View Option
[1]
文金磊 ,朱一民 ,周菁 ,等 铅锌矿产资源特征及浮选工艺研究现状
[J].矿产综合利用 ,2015 (6 ):1 -6 .
[本文引用: 1]
Wen Jinlei Zhu Yimin Zhou Jing et al Research status of Pb-Zn mineral resource characteristics and flotation technology
[J].Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources ,2015 (6 ):1 -6 .
[本文引用: 1]
[2]
国土资源部 中国矿产资源报告
[R].北京 :地质出版社 ,2017 :3 -4 .
[本文引用: 1]
Ministry of Land and Resources China mineral resources report
[R].Beijing :Geological Publishing House ,2017 :3 -4 .
[本文引用: 1]
[3]
薛亚洲 ,王海军 我国铅锌矿资源综合利用现状
[J].中国矿业 ,2005 ,14 (8 ):41 -42 .
[本文引用: 1]
Xue Yazhou Wang Haijun The status of lead and zinc ore comprehensive utilization in China
[J].China Mining Magazine ,2005 ,14 (8 ):41 -42 .
[本文引用: 1]
[4]
磨学诗 ,黄伟中 ,张雁生 ,等 提高多金属硫化铅锌矿浮选指标的研究
[J].有色金属(选矿部分) ,2007 (1 ):9 -12 .
[本文引用: 1]
Mo Xueshi Huang Weizhong Zhang Yansheng et al Study and practice on floatation of complex lead-zinc sulfide minerals for increasing floatation index
[J].Nonferrous Metals(Mineral Processing Section) ,2007 (1 ):9 -12 .
[本文引用: 1]
[5]
Liang Y Q Zhang X D Zhang H P et al Using a new bulk flotation process to enhance the recovery of mineral beneficiation in a lead-zinc sulfide-oxide mixed ore
[J].Advanced Materials Research ,2013 ,634-638 :3545 -3550 .
[本文引用: 1]
[6]
姜美光 ,刘全军 ,杨俊龙 ,等 新疆某硫化铅锌矿选矿试验研究
[J].矿冶 ,2014 ,23 (1 ):26 -30 .
[本文引用: 1]
Jiang Meiguang Liu Quanjun Yang Junlong et al Study on processing of a lead and zinc sulfide ore from Xinjiang Province
[J].Mining and Metallurgy ,2014 ,23 (1 ):26 -30 .
[本文引用: 1]
[7]
丘学民 ,陈国宝 ,张勤 ,等 从超细粒高铅锌氰化尾渣中浮选回收有价金属的试验研究
[J].黄金科学技术 ,2017 ,25 (6 ):61 -67 .
[本文引用: 1]
Qiu Xueming Chen Guobao Zhang Qin et al Experimental study on flotation recovery of valuable metals from ultrafine cyanide tailing containing high grade lead and zinc
[J].Gold Science and Technology ,2017 ,25 (6 ):61 -67 .
[本文引用: 1]
[8]
邱廷省 ,何元卿 ,余文 ,等 硫化铅锌矿浮选分离技术的研究现状及进展
[J].金属矿山 ,2016 ,45 (3 ):1 -9 .
[本文引用: 1]
Qiu Tingsheng He Yuanqing Yu Wen et al Research status and development of the lead-zinc sulfide ore flotation separation
[J].Metal Mine ,2016 ,45 (3 ):1 -9 .
[本文引用: 1]
[9]
焦学尧 ,樊小龙 ,余平辉 ,等 甘肃厂坝铅锌矿床黄铁矿流体包裹体He-Ar同位素体系
[J].黄金科学技术 ,2016 ,24 (4 ):47 -53 .
[本文引用: 1]
Jiao Xueyao Fan Xiaolong Yu Pinghui et al He-Ar isotopic system of fluid inclusions in pyrite from the Changba lead-zinc deposit in Gansu Province
[J].Cold Science and Technology ,2016 ,24 (4 ):47 -53 .
[本文引用: 1]
[10]
张培鼎 ,严维良 白石嶂钼矿3 kt/d选厂选矿工艺流程的分析
[J].有色金属工程 ,2011 ,1 (4 ):24 -28 .
[本文引用: 1]
Zhang Peiding Yan Weiliang The process of 3 kt/d Baishizhang molybdenum concentrator
[J].Nonferrous Metals Engineering ,2011 ,1 (4 ):24 -28 .
[本文引用: 1]
[11]
焦科诚 云南羊拉某低品位细粒级难选铜矿选矿试验研究
[J].有色矿冶 ,2013 ,29 (1 ):23 -26 .
[本文引用: 1]
Jiao Kecheng Benefication test research of a low grade,fine-grained refractory copper ore in Yangla,Yunnan Province
[J].Nonferrous Mining and metallurgy ,2013 ,29 (1 ):23 -26 .
[本文引用: 1]
[12]
Feng Q C Wen S M Zhao W J et al Recovery of molybdenum from molybdenum ore with a high content of carbon by separating carbon from sulfur
[J].Advanced Materials Research ,2013 ,634-638 :3450 -3453 .
[本文引用: 1]
[13]
方夕辉 ,曾怀远 ,陈文亮 ,等 新疆某复杂低品位氧化铅锌矿选矿工艺
[J].有色金属工程 ,2014 ,4 (2 ):49 -53 .
[本文引用: 1]
Fang Xihui Zeng Huaiyuan Chen Wenliang Beneficiation process of a complex low-grade lead-zinc ore in Xinjiang
[J].Nonferrous Metals Engineering ,2014 ,4 (2 ):49 -53 .
[本文引用: 1]
[14]
陈启如 ,孙广周 ,黄斌 ,等 云南某地硫化铅锌矿优先浮选分离试验研究
[J].矿产综合利用 ,2018 (4 ):62 -66 .
[本文引用: 1]
Chen Qiru Sun Guangzhou Huang Bin et al Experiment research on preferential flotation process for the lead-zinc ore from Yunnan
[J].Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources ,2018 (4 ):62 -66 .
[本文引用: 1]
[15]
雷阿丽 ,吴彩斌 ,江领培 某低品位伴生银铅锌多金属矿选矿工艺试验研究
[J].黄金科学技术 ,2018 ,26 (2 ):212 -218 .
[本文引用: 1]
Lei Ali Wu Caibin Jiang Lingpei Experiment research on beneficiation process of a low grade polymetallic lead-zinc ore with associated silver
[J].Gold Science and Technology ,2018 ,26 (2 ):212 -218 .
[本文引用: 1]
[16]
罗仙平 ,王金庆 ,曹志明 ,等 浮选粒度及浓度对铅锌硫化矿浮选分离的影响
[J].稀有金属 ,2018 ,42 (3 ):307 -314 .
[本文引用: 1]
Luo Xianping Wang Jinqing Cao Zhiming et al Flotation separation of lead-zinc sulfide ore with different flotation particle size and concentration
[J].Chinese Joural of Rare Metals ,2018 ,42 (3 ):307 -314 .
[本文引用: 1]
[17]
于涛 一段闭路磨矿分级旋流器与分级机的工业实践
[C]//全国矿山采选技术进展报告会 .呼和浩特 :全国冶金矿山信息网 ,2006 .
[本文引用: 1]
Yu Tao Industrial practice of classifying cyclones and classifiers for a closed-circuit grinding
[C]//National Mining Technology Progress Report .Hohhot :National Metallurgical Mine Information Network ,2016 .
[本文引用: 1]
[18]
沈同喜 ,余新阳 江西某铅锌多金属硫化矿石选矿试验研究
[J].有色金属科学与工程 ,2012 ,3 (2 ):71 -75 .
[本文引用: 1]
Shen Tongxi Yu Xinyang The processing experiment of a Pb-Zn multi-metal sulfide ore
[J].Nonferrous Metals Science and Engineering ,2012 ,3 (2 ):71 -75 .
[本文引用: 1]
[19]
魏宗武 ,陈建华 ,艾光华 ,等 硫化铅锌矿无氰浮选工艺流程及技术进展
[J].矿产保护与利用 ,2007 (4 ):39 -44 .
[本文引用: 1]
Wei Zongwu Chen Jianhua Ai Guanghua et al Development of cyanide-free flotation flowsheet and technology for lead and zinc sulfide ores
[J].Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources ,2007 (4 ):39 -44 .
[本文引用: 1]
[20]
肖骏 ,陈代雄 ,杨建文 ,等 凡口铅锌矿铅锌硫混合精矿分离试验研究
[J].有色金属科学与工程 ,2015 ,6 (2 ):104 -110 .
[本文引用: 1]
Xiao Jun Chen Daixiong Yang Jianwen et al Separation tests of the lead-zinc-sulfur mixed concentrate in Fankou lead and zinc mine
[J].Nonferrous Metals Science and Engineering ,2016 ,6 (2 ):104 -110 .
[本文引用: 1]
[21]
余新阳 ,王浩林 ,王强强 ,等 江西某伴生银难选铅锌矿浮选分离
[J].有色金属工程 ,2016 ,6 (5 ):49 -54 .
[本文引用: 1]
Yu Xinyang Wang Haolin Wang Qiangqiang et al Flotation separation of a lead-zinc ore with associated silver from Jiangxi
[J].Nonferrous Metals Engineering ,2016 ,6 (5 ):49 -54 .
[本文引用: 1]
[22]
常富强 ,段德华 ,宋龑 生产中提高球磨机磨矿效率的方法
[J].现代矿业 ,2011 (3 ):81 -84 .
[本文引用: 1]
Chang Fuqiang Duan Dehua Song Yan Method for improving grinding efficiency of ball mill in production
[J].Modern Mining ,2011 (3 ):81 -84 .
[本文引用: 1]
[23]
周贺鹏 ,雷梅芬 ,罗礼英 ,等 广西某铜铋硫化矿选矿新工艺研究
[J].矿业研究与开发 ,2013 ,33 (1 ):52 -55 .
[本文引用: 1]
Zhou Hepeng Lei Meifen Luo Liying et al Study on the new benefication process of a copper bismuth sulphide ore from Guangxi
[J].Mining Research and Development ,2013 ,33 (1 ):52 -55 .
[本文引用: 1]
[24]
贺国帅 ,陈代雄 ,杨建文 ,等 湖南鲁塘隐晶质石墨矿选矿试验研究
[J].矿产保护与利用 ,2018 (5 ):63 -67 .
[本文引用: 1]
He Guoshuai Chen Daixiong Yang Jianwen et al Experimental study on the beneficiation of aphanitic graphite ore from Lutang in Hunan
[J].Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources ,2018 (5 ):63 -67 .
[本文引用: 1]
铅锌矿产资源特征及浮选工艺研究现状
1
... 铅锌是国民经济与科技发展的保障性资源,铅锌矿产资源的高效开发利用是国家重大战略需求[1 ] .我国铅锌资源丰富,已查明的铅金属量达8 546.77×104 t,锌金属量达17 798.89×104 t[2 ] ,但目前开发的铅锌矿床中,大多矿石类型复杂,共伴生组分多[3 ,4 ,5 ] ,综合回收难度大,而铅锌硫化矿物(如方铅矿、闪锌矿和黄铁矿等)界面性质相近,浮选分离存在一定的困难[6 ] ,导致该类资源高效综合利用难度增加.随着国民经济的发展,各行业对铅锌资源的需求量也在不断增加,需进一步加强对铅锌资源合理、高效的开发利用[7 ,8 ] . ...
铅锌矿产资源特征及浮选工艺研究现状
1
... 铅锌是国民经济与科技发展的保障性资源,铅锌矿产资源的高效开发利用是国家重大战略需求[1 ] .我国铅锌资源丰富,已查明的铅金属量达8 546.77×104 t,锌金属量达17 798.89×104 t[2 ] ,但目前开发的铅锌矿床中,大多矿石类型复杂,共伴生组分多[3 ,4 ,5 ] ,综合回收难度大,而铅锌硫化矿物(如方铅矿、闪锌矿和黄铁矿等)界面性质相近,浮选分离存在一定的困难[6 ] ,导致该类资源高效综合利用难度增加.随着国民经济的发展,各行业对铅锌资源的需求量也在不断增加,需进一步加强对铅锌资源合理、高效的开发利用[7 ,8 ] . ...
中国矿产资源报告
1
2017
... 铅锌是国民经济与科技发展的保障性资源,铅锌矿产资源的高效开发利用是国家重大战略需求[1 ] .我国铅锌资源丰富,已查明的铅金属量达8 546.77×104 t,锌金属量达17 798.89×104 t[2 ] ,但目前开发的铅锌矿床中,大多矿石类型复杂,共伴生组分多[3 ,4 ,5 ] ,综合回收难度大,而铅锌硫化矿物(如方铅矿、闪锌矿和黄铁矿等)界面性质相近,浮选分离存在一定的困难[6 ] ,导致该类资源高效综合利用难度增加.随着国民经济的发展,各行业对铅锌资源的需求量也在不断增加,需进一步加强对铅锌资源合理、高效的开发利用[7 ,8 ] . ...
中国矿产资源报告
1
2017
... 铅锌是国民经济与科技发展的保障性资源,铅锌矿产资源的高效开发利用是国家重大战略需求[1 ] .我国铅锌资源丰富,已查明的铅金属量达8 546.77×104 t,锌金属量达17 798.89×104 t[2 ] ,但目前开发的铅锌矿床中,大多矿石类型复杂,共伴生组分多[3 ,4 ,5 ] ,综合回收难度大,而铅锌硫化矿物(如方铅矿、闪锌矿和黄铁矿等)界面性质相近,浮选分离存在一定的困难[6 ] ,导致该类资源高效综合利用难度增加.随着国民经济的发展,各行业对铅锌资源的需求量也在不断增加,需进一步加强对铅锌资源合理、高效的开发利用[7 ,8 ] . ...
我国铅锌矿资源综合利用现状
1
2005
... 铅锌是国民经济与科技发展的保障性资源,铅锌矿产资源的高效开发利用是国家重大战略需求[1 ] .我国铅锌资源丰富,已查明的铅金属量达8 546.77×104 t,锌金属量达17 798.89×104 t[2 ] ,但目前开发的铅锌矿床中,大多矿石类型复杂,共伴生组分多[3 ,4 ,5 ] ,综合回收难度大,而铅锌硫化矿物(如方铅矿、闪锌矿和黄铁矿等)界面性质相近,浮选分离存在一定的困难[6 ] ,导致该类资源高效综合利用难度增加.随着国民经济的发展,各行业对铅锌资源的需求量也在不断增加,需进一步加强对铅锌资源合理、高效的开发利用[7 ,8 ] . ...
我国铅锌矿资源综合利用现状
1
2005
... 铅锌是国民经济与科技发展的保障性资源,铅锌矿产资源的高效开发利用是国家重大战略需求[1 ] .我国铅锌资源丰富,已查明的铅金属量达8 546.77×104 t,锌金属量达17 798.89×104 t[2 ] ,但目前开发的铅锌矿床中,大多矿石类型复杂,共伴生组分多[3 ,4 ,5 ] ,综合回收难度大,而铅锌硫化矿物(如方铅矿、闪锌矿和黄铁矿等)界面性质相近,浮选分离存在一定的困难[6 ] ,导致该类资源高效综合利用难度增加.随着国民经济的发展,各行业对铅锌资源的需求量也在不断增加,需进一步加强对铅锌资源合理、高效的开发利用[7 ,8 ] . ...
提高多金属硫化铅锌矿浮选指标的研究
1
... 铅锌是国民经济与科技发展的保障性资源,铅锌矿产资源的高效开发利用是国家重大战略需求[1 ] .我国铅锌资源丰富,已查明的铅金属量达8 546.77×104 t,锌金属量达17 798.89×104 t[2 ] ,但目前开发的铅锌矿床中,大多矿石类型复杂,共伴生组分多[3 ,4 ,5 ] ,综合回收难度大,而铅锌硫化矿物(如方铅矿、闪锌矿和黄铁矿等)界面性质相近,浮选分离存在一定的困难[6 ] ,导致该类资源高效综合利用难度增加.随着国民经济的发展,各行业对铅锌资源的需求量也在不断增加,需进一步加强对铅锌资源合理、高效的开发利用[7 ,8 ] . ...
提高多金属硫化铅锌矿浮选指标的研究
1
... 铅锌是国民经济与科技发展的保障性资源,铅锌矿产资源的高效开发利用是国家重大战略需求[1 ] .我国铅锌资源丰富,已查明的铅金属量达8 546.77×104 t,锌金属量达17 798.89×104 t[2 ] ,但目前开发的铅锌矿床中,大多矿石类型复杂,共伴生组分多[3 ,4 ,5 ] ,综合回收难度大,而铅锌硫化矿物(如方铅矿、闪锌矿和黄铁矿等)界面性质相近,浮选分离存在一定的困难[6 ] ,导致该类资源高效综合利用难度增加.随着国民经济的发展,各行业对铅锌资源的需求量也在不断增加,需进一步加强对铅锌资源合理、高效的开发利用[7 ,8 ] . ...
Using a new bulk flotation process to enhance the recovery of mineral beneficiation in a lead-zinc sulfide-oxide mixed ore
1
2013
... 铅锌是国民经济与科技发展的保障性资源,铅锌矿产资源的高效开发利用是国家重大战略需求[1 ] .我国铅锌资源丰富,已查明的铅金属量达8 546.77×104 t,锌金属量达17 798.89×104 t[2 ] ,但目前开发的铅锌矿床中,大多矿石类型复杂,共伴生组分多[3 ,4 ,5 ] ,综合回收难度大,而铅锌硫化矿物(如方铅矿、闪锌矿和黄铁矿等)界面性质相近,浮选分离存在一定的困难[6 ] ,导致该类资源高效综合利用难度增加.随着国民经济的发展,各行业对铅锌资源的需求量也在不断增加,需进一步加强对铅锌资源合理、高效的开发利用[7 ,8 ] . ...
新疆某硫化铅锌矿选矿试验研究
1
2014
... 铅锌是国民经济与科技发展的保障性资源,铅锌矿产资源的高效开发利用是国家重大战略需求[1 ] .我国铅锌资源丰富,已查明的铅金属量达8 546.77×104 t,锌金属量达17 798.89×104 t[2 ] ,但目前开发的铅锌矿床中,大多矿石类型复杂,共伴生组分多[3 ,4 ,5 ] ,综合回收难度大,而铅锌硫化矿物(如方铅矿、闪锌矿和黄铁矿等)界面性质相近,浮选分离存在一定的困难[6 ] ,导致该类资源高效综合利用难度增加.随着国民经济的发展,各行业对铅锌资源的需求量也在不断增加,需进一步加强对铅锌资源合理、高效的开发利用[7 ,8 ] . ...
新疆某硫化铅锌矿选矿试验研究
1
2014
... 铅锌是国民经济与科技发展的保障性资源,铅锌矿产资源的高效开发利用是国家重大战略需求[1 ] .我国铅锌资源丰富,已查明的铅金属量达8 546.77×104 t,锌金属量达17 798.89×104 t[2 ] ,但目前开发的铅锌矿床中,大多矿石类型复杂,共伴生组分多[3 ,4 ,5 ] ,综合回收难度大,而铅锌硫化矿物(如方铅矿、闪锌矿和黄铁矿等)界面性质相近,浮选分离存在一定的困难[6 ] ,导致该类资源高效综合利用难度增加.随着国民经济的发展,各行业对铅锌资源的需求量也在不断增加,需进一步加强对铅锌资源合理、高效的开发利用[7 ,8 ] . ...
从超细粒高铅锌氰化尾渣中浮选回收有价金属的试验研究
1
2017
... 铅锌是国民经济与科技发展的保障性资源,铅锌矿产资源的高效开发利用是国家重大战略需求[1 ] .我国铅锌资源丰富,已查明的铅金属量达8 546.77×104 t,锌金属量达17 798.89×104 t[2 ] ,但目前开发的铅锌矿床中,大多矿石类型复杂,共伴生组分多[3 ,4 ,5 ] ,综合回收难度大,而铅锌硫化矿物(如方铅矿、闪锌矿和黄铁矿等)界面性质相近,浮选分离存在一定的困难[6 ] ,导致该类资源高效综合利用难度增加.随着国民经济的发展,各行业对铅锌资源的需求量也在不断增加,需进一步加强对铅锌资源合理、高效的开发利用[7 ,8 ] . ...
从超细粒高铅锌氰化尾渣中浮选回收有价金属的试验研究
1
2017
... 铅锌是国民经济与科技发展的保障性资源,铅锌矿产资源的高效开发利用是国家重大战略需求[1 ] .我国铅锌资源丰富,已查明的铅金属量达8 546.77×104 t,锌金属量达17 798.89×104 t[2 ] ,但目前开发的铅锌矿床中,大多矿石类型复杂,共伴生组分多[3 ,4 ,5 ] ,综合回收难度大,而铅锌硫化矿物(如方铅矿、闪锌矿和黄铁矿等)界面性质相近,浮选分离存在一定的困难[6 ] ,导致该类资源高效综合利用难度增加.随着国民经济的发展,各行业对铅锌资源的需求量也在不断增加,需进一步加强对铅锌资源合理、高效的开发利用[7 ,8 ] . ...
硫化铅锌矿浮选分离技术的研究现状及进展
1
2016
... 铅锌是国民经济与科技发展的保障性资源,铅锌矿产资源的高效开发利用是国家重大战略需求[1 ] .我国铅锌资源丰富,已查明的铅金属量达8 546.77×104 t,锌金属量达17 798.89×104 t[2 ] ,但目前开发的铅锌矿床中,大多矿石类型复杂,共伴生组分多[3 ,4 ,5 ] ,综合回收难度大,而铅锌硫化矿物(如方铅矿、闪锌矿和黄铁矿等)界面性质相近,浮选分离存在一定的困难[6 ] ,导致该类资源高效综合利用难度增加.随着国民经济的发展,各行业对铅锌资源的需求量也在不断增加,需进一步加强对铅锌资源合理、高效的开发利用[7 ,8 ] . ...
硫化铅锌矿浮选分离技术的研究现状及进展
1
2016
... 铅锌是国民经济与科技发展的保障性资源,铅锌矿产资源的高效开发利用是国家重大战略需求[1 ] .我国铅锌资源丰富,已查明的铅金属量达8 546.77×104 t,锌金属量达17 798.89×104 t[2 ] ,但目前开发的铅锌矿床中,大多矿石类型复杂,共伴生组分多[3 ,4 ,5 ] ,综合回收难度大,而铅锌硫化矿物(如方铅矿、闪锌矿和黄铁矿等)界面性质相近,浮选分离存在一定的困难[6 ] ,导致该类资源高效综合利用难度增加.随着国民经济的发展,各行业对铅锌资源的需求量也在不断增加,需进一步加强对铅锌资源合理、高效的开发利用[7 ,8 ] . ...
甘肃厂坝铅锌矿床黄铁矿流体包裹体He-Ar同位素体系
1
2016
... 甘肃洛坝铅锌矿是一座含铅锌且伴生有少量银、硫的泥岩—细碎屑岩型铅锌矿床[9 ,10 ] ,近年来随着铅锌资源的不断开发,铅锌矿石性质发生显著变化,铅、锌品位下降,而C、Si和Fe等杂质元素含量明显升高,使得选矿生产存在铅精矿品位下降、锌精矿含硅超标等问题.为查明精矿质量下降的原因,以及选矿流程中可能存在的问题,探索铅锌浮选回收的难点及物性因素,进行系统的选矿流程考察和矿石性质分析,以期为该铅锌资源的高效回收提供有益指导. ...
甘肃厂坝铅锌矿床黄铁矿流体包裹体He-Ar同位素体系
1
2016
... 甘肃洛坝铅锌矿是一座含铅锌且伴生有少量银、硫的泥岩—细碎屑岩型铅锌矿床[9 ,10 ] ,近年来随着铅锌资源的不断开发,铅锌矿石性质发生显著变化,铅、锌品位下降,而C、Si和Fe等杂质元素含量明显升高,使得选矿生产存在铅精矿品位下降、锌精矿含硅超标等问题.为查明精矿质量下降的原因,以及选矿流程中可能存在的问题,探索铅锌浮选回收的难点及物性因素,进行系统的选矿流程考察和矿石性质分析,以期为该铅锌资源的高效回收提供有益指导. ...
白石嶂钼矿3 kt/d选厂选矿工艺流程的分析
1
2011
... 甘肃洛坝铅锌矿是一座含铅锌且伴生有少量银、硫的泥岩—细碎屑岩型铅锌矿床[9 ,10 ] ,近年来随着铅锌资源的不断开发,铅锌矿石性质发生显著变化,铅、锌品位下降,而C、Si和Fe等杂质元素含量明显升高,使得选矿生产存在铅精矿品位下降、锌精矿含硅超标等问题.为查明精矿质量下降的原因,以及选矿流程中可能存在的问题,探索铅锌浮选回收的难点及物性因素,进行系统的选矿流程考察和矿石性质分析,以期为该铅锌资源的高效回收提供有益指导. ...
白石嶂钼矿3 kt/d选厂选矿工艺流程的分析
1
2011
... 甘肃洛坝铅锌矿是一座含铅锌且伴生有少量银、硫的泥岩—细碎屑岩型铅锌矿床[9 ,10 ] ,近年来随着铅锌资源的不断开发,铅锌矿石性质发生显著变化,铅、锌品位下降,而C、Si和Fe等杂质元素含量明显升高,使得选矿生产存在铅精矿品位下降、锌精矿含硅超标等问题.为查明精矿质量下降的原因,以及选矿流程中可能存在的问题,探索铅锌浮选回收的难点及物性因素,进行系统的选矿流程考察和矿石性质分析,以期为该铅锌资源的高效回收提供有益指导. ...
云南羊拉某低品位细粒级难选铜矿选矿试验研究
1
2013
... 由表1 可知,Pb和Zn是洛坝矿主要的回收元素;伴生的Cu、S和Ag等元素含量低,回收价值不大;矿石中碳质含量较高,因其具较好的可浮性和吸附性能,对铅锌选别产生较大影响[11 ,12 ] ;由CaO、SiO2 、Al2 O3 和MgO等化合物组成的碳酸盐—硅酸盐类矿物属于脉石矿物,其易碎磨泥化,对铅锌精矿产生干扰[13 ] ;此外,矿石中Fe含量较高,主要以菱铁矿形式存在,难以通过选矿回收. ...
云南羊拉某低品位细粒级难选铜矿选矿试验研究
1
2013
... 由表1 可知,Pb和Zn是洛坝矿主要的回收元素;伴生的Cu、S和Ag等元素含量低,回收价值不大;矿石中碳质含量较高,因其具较好的可浮性和吸附性能,对铅锌选别产生较大影响[11 ,12 ] ;由CaO、SiO2 、Al2 O3 和MgO等化合物组成的碳酸盐—硅酸盐类矿物属于脉石矿物,其易碎磨泥化,对铅锌精矿产生干扰[13 ] ;此外,矿石中Fe含量较高,主要以菱铁矿形式存在,难以通过选矿回收. ...
Recovery of molybdenum from molybdenum ore with a high content of carbon by separating carbon from sulfur
1
2013
... 由表1 可知,Pb和Zn是洛坝矿主要的回收元素;伴生的Cu、S和Ag等元素含量低,回收价值不大;矿石中碳质含量较高,因其具较好的可浮性和吸附性能,对铅锌选别产生较大影响[11 ,12 ] ;由CaO、SiO2 、Al2 O3 和MgO等化合物组成的碳酸盐—硅酸盐类矿物属于脉石矿物,其易碎磨泥化,对铅锌精矿产生干扰[13 ] ;此外,矿石中Fe含量较高,主要以菱铁矿形式存在,难以通过选矿回收. ...
新疆某复杂低品位氧化铅锌矿选矿工艺
1
2014
... 由表1 可知,Pb和Zn是洛坝矿主要的回收元素;伴生的Cu、S和Ag等元素含量低,回收价值不大;矿石中碳质含量较高,因其具较好的可浮性和吸附性能,对铅锌选别产生较大影响[11 ,12 ] ;由CaO、SiO2 、Al2 O3 和MgO等化合物组成的碳酸盐—硅酸盐类矿物属于脉石矿物,其易碎磨泥化,对铅锌精矿产生干扰[13 ] ;此外,矿石中Fe含量较高,主要以菱铁矿形式存在,难以通过选矿回收. ...
新疆某复杂低品位氧化铅锌矿选矿工艺
1
2014
... 由表1 可知,Pb和Zn是洛坝矿主要的回收元素;伴生的Cu、S和Ag等元素含量低,回收价值不大;矿石中碳质含量较高,因其具较好的可浮性和吸附性能,对铅锌选别产生较大影响[11 ,12 ] ;由CaO、SiO2 、Al2 O3 和MgO等化合物组成的碳酸盐—硅酸盐类矿物属于脉石矿物,其易碎磨泥化,对铅锌精矿产生干扰[13 ] ;此外,矿石中Fe含量较高,主要以菱铁矿形式存在,难以通过选矿回收. ...
云南某地硫化铅锌矿优先浮选分离试验研究
1
... 矿石中铅、锌得到了较好的富集回收,但与其他相似铅锌矿相比[14 ,15 ] ,铅锌精矿的品位仍有一定的提升空间,且铅锌精矿中硅含量较高,影响产品质量,因此需进行系统的选矿工艺流程考察,找出影响铅、锌选别的主要因素及其解决方案. ...
云南某地硫化铅锌矿优先浮选分离试验研究
1
... 矿石中铅、锌得到了较好的富集回收,但与其他相似铅锌矿相比[14 ,15 ] ,铅锌精矿的品位仍有一定的提升空间,且铅锌精矿中硅含量较高,影响产品质量,因此需进行系统的选矿工艺流程考察,找出影响铅、锌选别的主要因素及其解决方案. ...
某低品位伴生银铅锌多金属矿选矿工艺试验研究
1
2018
... 矿石中铅、锌得到了较好的富集回收,但与其他相似铅锌矿相比[14 ,15 ] ,铅锌精矿的品位仍有一定的提升空间,且铅锌精矿中硅含量较高,影响产品质量,因此需进行系统的选矿工艺流程考察,找出影响铅、锌选别的主要因素及其解决方案. ...
某低品位伴生银铅锌多金属矿选矿工艺试验研究
1
2018
... 矿石中铅、锌得到了较好的富集回收,但与其他相似铅锌矿相比[14 ,15 ] ,铅锌精矿的品位仍有一定的提升空间,且铅锌精矿中硅含量较高,影响产品质量,因此需进行系统的选矿工艺流程考察,找出影响铅、锌选别的主要因素及其解决方案. ...
浮选粒度及浓度对铅锌硫化矿浮选分离的影响
1
2018
... 原矿经一段闭路磨矿后螺旋分级机溢流产品中-74 μm粒级占69.33%,-45 μm粒级占55.19%,远超过正常的细粒分布水平[16 ] .+45 μm粒级铅含量较低,质量分数在0.10%~0.13%范围内,而-45 μm粒级铅质量分数高达1%,相比原矿富集了近一倍,而在此微细粒级中铅分布率高达91.03%,表明铅矿物易于碎磨和解离,这种碎磨和嵌布特性有利于铅的浮选回收.然而,由于绝大多数铅的入选粒级为-45 μm微细粒级,不利于铅与其他微细粒脉石矿物及易浮杂质矿物等之间的分离,影响了铅精矿品位的提高.锌和杂质硅矿物在各粒级中的品位分布较均匀,差异不大. ...
浮选粒度及浓度对铅锌硫化矿浮选分离的影响
1
2018
... 原矿经一段闭路磨矿后螺旋分级机溢流产品中-74 μm粒级占69.33%,-45 μm粒级占55.19%,远超过正常的细粒分布水平[16 ] .+45 μm粒级铅含量较低,质量分数在0.10%~0.13%范围内,而-45 μm粒级铅质量分数高达1%,相比原矿富集了近一倍,而在此微细粒级中铅分布率高达91.03%,表明铅矿物易于碎磨和解离,这种碎磨和嵌布特性有利于铅的浮选回收.然而,由于绝大多数铅的入选粒级为-45 μm微细粒级,不利于铅与其他微细粒脉石矿物及易浮杂质矿物等之间的分离,影响了铅精矿品位的提高.锌和杂质硅矿物在各粒级中的品位分布较均匀,差异不大. ...
一段闭路磨矿分级旋流器与分级机的工业实践
1
2016
... 螺旋分级机的返砂比为73.39%,而一段闭路磨矿分级机的返砂比通常在150%~350%之间[17 ] ,由此可见螺旋分级机的返砂比严重偏低,循环负荷量较小,这不仅影响球磨机的磨矿效率,而且易加重细粒矿物过粉碎现象. ...
一段闭路磨矿分级旋流器与分级机的工业实践
1
2016
... 螺旋分级机的返砂比为73.39%,而一段闭路磨矿分级机的返砂比通常在150%~350%之间[17 ] ,由此可见螺旋分级机的返砂比严重偏低,循环负荷量较小,这不仅影响球磨机的磨矿效率,而且易加重细粒矿物过粉碎现象. ...
江西某铅锌多金属硫化矿石选矿试验研究
1
2012
... 铅精矿中所含的锌主要为细粒级,因此要降低铅精矿中的锌含量,需从细粒级锌矿物入手,添加少量的抑制剂进行细粒锌的强化抑制[18 ,19 ] .锌在锌精矿和总尾矿中的分布基本一致,以细粒级为主.锌精矿中回收的锌主要为细粒级,且尾矿中损失的锌矿物更细,为进一步提高锌回收率,需从细粒级入手,强化细粒锌的回收. ...
江西某铅锌多金属硫化矿石选矿试验研究
1
2012
... 铅精矿中所含的锌主要为细粒级,因此要降低铅精矿中的锌含量,需从细粒级锌矿物入手,添加少量的抑制剂进行细粒锌的强化抑制[18 ,19 ] .锌在锌精矿和总尾矿中的分布基本一致,以细粒级为主.锌精矿中回收的锌主要为细粒级,且尾矿中损失的锌矿物更细,为进一步提高锌回收率,需从细粒级入手,强化细粒锌的回收. ...
硫化铅锌矿无氰浮选工艺流程及技术进展
1
... 铅精矿中所含的锌主要为细粒级,因此要降低铅精矿中的锌含量,需从细粒级锌矿物入手,添加少量的抑制剂进行细粒锌的强化抑制[18 ,19 ] .锌在锌精矿和总尾矿中的分布基本一致,以细粒级为主.锌精矿中回收的锌主要为细粒级,且尾矿中损失的锌矿物更细,为进一步提高锌回收率,需从细粒级入手,强化细粒锌的回收. ...
硫化铅锌矿无氰浮选工艺流程及技术进展
1
... 铅精矿中所含的锌主要为细粒级,因此要降低铅精矿中的锌含量,需从细粒级锌矿物入手,添加少量的抑制剂进行细粒锌的强化抑制[18 ,19 ] .锌在锌精矿和总尾矿中的分布基本一致,以细粒级为主.锌精矿中回收的锌主要为细粒级,且尾矿中损失的锌矿物更细,为进一步提高锌回收率,需从细粒级入手,强化细粒锌的回收. ...
凡口铅锌矿铅锌硫混合精矿分离试验研究
1
2016
... (2)入磨矿石细粒物料偏多,筛分工艺有待优化.入磨给料皮带上粉状细粒矿石增多,其中-74 μm粒级含量达7.68%,-150 μm粒级含量更高,而现有筛分工艺未根据原矿粒度组成制定相应的筛分流程,直接将细粒物料与粗粒矿石一并入磨,加剧了细粒矿石的过磨现象[20 ] ,导致分级溢流中-38 μm微细粒级含量增多,达48.88%.建议增加一套2 mm的细筛湿筛,将筛下产品与磨矿产品合并,同时给入螺旋分级机分级,及时分离出合格粒级,减少过磨现象. ...
凡口铅锌矿铅锌硫混合精矿分离试验研究
1
2016
... (2)入磨矿石细粒物料偏多,筛分工艺有待优化.入磨给料皮带上粉状细粒矿石增多,其中-74 μm粒级含量达7.68%,-150 μm粒级含量更高,而现有筛分工艺未根据原矿粒度组成制定相应的筛分流程,直接将细粒物料与粗粒矿石一并入磨,加剧了细粒矿石的过磨现象[20 ] ,导致分级溢流中-38 μm微细粒级含量增多,达48.88%.建议增加一套2 mm的细筛湿筛,将筛下产品与磨矿产品合并,同时给入螺旋分级机分级,及时分离出合格粒级,减少过磨现象. ...
江西某伴生银难选铅锌矿浮选分离
1
2016
... (3)磨矿工艺过粉碎严重,磨矿参数有待优化.原矿属于低铅锌含碳的碳酸盐—硅酸盐混合型铅锌矿,矿石中石英、闪石和长石等硅酸盐脉石矿物难以碎磨,而隐晶质石墨、方解石、云母和方铅矿等易于碎磨,且铅锌矿物普遍呈粒状和块状等构造沿脉石矿物裂隙充填或交代连生,易造成铅、锌及部分隐晶质石墨、方解石和云母等矿物易于过磨.而铅锌及脉石矿物的过粉碎,不仅造成浮选矿浆黏度增加,而且微细粒矿物间的分离难度增大,碳质及细粒脉石粘滞夹带或疏水上浮进入精矿,影响精矿品位和质量[21 ] .基于此类矿石性质,考虑到磨机排矿中-74 μm含量已达43.93%,现场进一步降低磨矿浓度(由目前的75%降低至70%),显著减轻细粒矿石的过粉碎现象. ...
江西某伴生银难选铅锌矿浮选分离
1
2016
... (3)磨矿工艺过粉碎严重,磨矿参数有待优化.原矿属于低铅锌含碳的碳酸盐—硅酸盐混合型铅锌矿,矿石中石英、闪石和长石等硅酸盐脉石矿物难以碎磨,而隐晶质石墨、方解石、云母和方铅矿等易于碎磨,且铅锌矿物普遍呈粒状和块状等构造沿脉石矿物裂隙充填或交代连生,易造成铅、锌及部分隐晶质石墨、方解石和云母等矿物易于过磨.而铅锌及脉石矿物的过粉碎,不仅造成浮选矿浆黏度增加,而且微细粒矿物间的分离难度增大,碳质及细粒脉石粘滞夹带或疏水上浮进入精矿,影响精矿品位和质量[21 ] .基于此类矿石性质,考虑到磨机排矿中-74 μm含量已达43.93%,现场进一步降低磨矿浓度(由目前的75%降低至70%),显著减轻细粒矿石的过粉碎现象. ...
生产中提高球磨机磨矿效率的方法
1
... (4)返砂比与分级效率偏低,分级参数有待调整.螺旋分级机返砂比为73.39%,比正常值(150%~350%)明显偏低,这不仅影响磨机的磨矿效率,而且易加重细粒级过粉碎[22 ] ,主要原因是球磨机选型偏大和矿石易磨碎,使得矿石在球磨机一次性磨细概率增大,造成返砂量减小而微细粒级增多.计算的分级质效率为59.47%,比螺旋分级机普遍正常值(60%~65%)略低,主要原因是分级浓度偏低,如分级溢流浓度仅为36.23%,比正常值(38%~42%)偏低.因此,可适度调小磨机排矿口水量,以提高进入分级机的分级浓度[23 ] . ...
生产中提高球磨机磨矿效率的方法
1
... (4)返砂比与分级效率偏低,分级参数有待调整.螺旋分级机返砂比为73.39%,比正常值(150%~350%)明显偏低,这不仅影响磨机的磨矿效率,而且易加重细粒级过粉碎[22 ] ,主要原因是球磨机选型偏大和矿石易磨碎,使得矿石在球磨机一次性磨细概率增大,造成返砂量减小而微细粒级增多.计算的分级质效率为59.47%,比螺旋分级机普遍正常值(60%~65%)略低,主要原因是分级浓度偏低,如分级溢流浓度仅为36.23%,比正常值(38%~42%)偏低.因此,可适度调小磨机排矿口水量,以提高进入分级机的分级浓度[23 ] . ...
广西某铜铋硫化矿选矿新工艺研究
1
2013
... (4)返砂比与分级效率偏低,分级参数有待调整.螺旋分级机返砂比为73.39%,比正常值(150%~350%)明显偏低,这不仅影响磨机的磨矿效率,而且易加重细粒级过粉碎[22 ] ,主要原因是球磨机选型偏大和矿石易磨碎,使得矿石在球磨机一次性磨细概率增大,造成返砂量减小而微细粒级增多.计算的分级质效率为59.47%,比螺旋分级机普遍正常值(60%~65%)略低,主要原因是分级浓度偏低,如分级溢流浓度仅为36.23%,比正常值(38%~42%)偏低.因此,可适度调小磨机排矿口水量,以提高进入分级机的分级浓度[23 ] . ...
广西某铜铋硫化矿选矿新工艺研究
1
2013
... (4)返砂比与分级效率偏低,分级参数有待调整.螺旋分级机返砂比为73.39%,比正常值(150%~350%)明显偏低,这不仅影响磨机的磨矿效率,而且易加重细粒级过粉碎[22 ] ,主要原因是球磨机选型偏大和矿石易磨碎,使得矿石在球磨机一次性磨细概率增大,造成返砂量减小而微细粒级增多.计算的分级质效率为59.47%,比螺旋分级机普遍正常值(60%~65%)略低,主要原因是分级浓度偏低,如分级溢流浓度仅为36.23%,比正常值(38%~42%)偏低.因此,可适度调小磨机排矿口水量,以提高进入分级机的分级浓度[23 ] . ...
湖南鲁塘隐晶质石墨矿选矿试验研究
1
... (5)开发高选择性药剂,降低浮选过程的泡沫黏度,从而提高铅、锌精矿品位和质量.铅、锌精矿单体含量分别为94.4%和90.9%,铅精矿中的锌与锌精矿中的铅主要呈连生体形态,部分黄铁矿为连生体,脉石矿物普遍为隐晶质石墨、石英、方解石和云母等,但铅精矿中碳质脉石矿物含量更高,锌精矿中硅质脉石矿物含量更高;铅、锌精矿中黄铁矿与脉石矿物杂质粒度微细(0.01~0.05 mm).据此,要实现铅、锌精矿品位的进一步提高,需强化含硅脉石矿物的抑制,而隐晶质石墨和黄铁矿通过降低矿浆与泡沫黏度的方式来解决[24 ] . ...
湖南鲁塘隐晶质石墨矿选矿试验研究
1
... (5)开发高选择性药剂,降低浮选过程的泡沫黏度,从而提高铅、锌精矿品位和质量.铅、锌精矿单体含量分别为94.4%和90.9%,铅精矿中的锌与锌精矿中的铅主要呈连生体形态,部分黄铁矿为连生体,脉石矿物普遍为隐晶质石墨、石英、方解石和云母等,但铅精矿中碳质脉石矿物含量更高,锌精矿中硅质脉石矿物含量更高;铅、锌精矿中黄铁矿与脉石矿物杂质粒度微细(0.01~0.05 mm).据此,要实现铅、锌精矿品位的进一步提高,需强化含硅脉石矿物的抑制,而隐晶质石墨和黄铁矿通过降低矿浆与泡沫黏度的方式来解决[24 ] . ...




 甘公网安备 62010202000672号
甘公网安备 62010202000672号